Background
There currently are no effective clinical treatments for correcting ischemic injury in patients, which is the basis for many serious medical conditions including shock, trauma, resuscitation injury, critical illness, heart failure, organ transplantation, and more. PM-208 aims to be a disruptive technology because it is geometrically more effective than standard of care, including whole blood, and because it operates on a mechanism of action that has not been appreciated in the past.
Mechanism of Action
PM-208 IV solution's mechanism of action in severe hypovolemic shock is the non-energetic unidirectional transfer of isotonic water out of ischemically swollen tissues and into capillaries by the establishments of dual osmotic gradients in the microcirculation. The resolution of tissue metabolic edema (incurred from ischemia during shock) decompresses the microcirculation and reloads the local capillaries with volume. Both of these effects re-establish efficient blood flow through tissue capillaries (perfusion), which enhances oxygen transfer to ischemic tissues and cells.
In research studies PM-208 has been shown to be highly effective in treating hemorrhagic shock in preclinical models, compared to Hextend and fresh whole blood. In swine suffering acute lethal hemorrhage of 55-60% blood loss, those resuscitated with PM-208 IV solution survived over a week after resuscitation, but the controls resuscitated with the same volume of LR (Lactated Ringers) solution or fresh whole autologous blood all died within 2-3 hours after treatment.

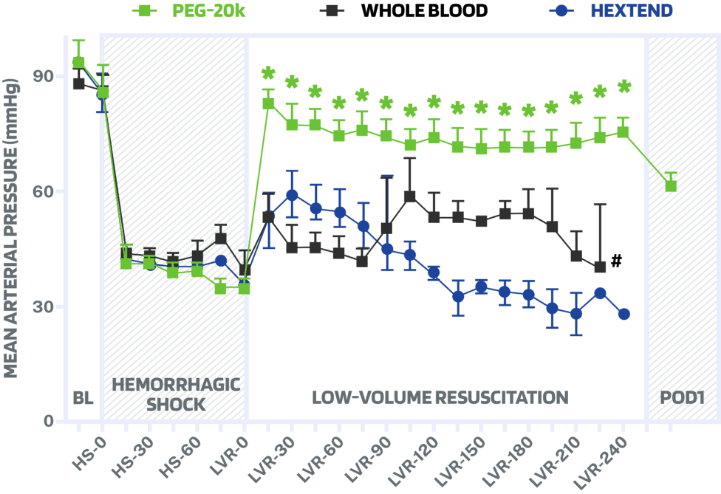
Research conducted at Virginia Commonwealth University and published in the Annals of Surgery illustrate some of the powerful impacts that PM-208's main component PEG-20k has in an animal model of hemorrhagic shock. Figure: Mean arterial blood pressure response after lethal hemorrhage in shocked swine resuscitated with Hextend, whole blood, and PM-208 I.V. solution. Only PM-208 resuscitated swine survived after 24 hours (Post-Op Day-1, POD1). *<0.05 relative to other corresponding values, n=6 per group. (Link to AOS paper)
Potential Applications for PM-208
In addition to hemorrhagic shock, research suggests that PM-208's biological mechanism of action could help patients experiencing other clinical events including cardiac illness, critical illness, sepsis, and vascular disease.
The BasicsMilitary and Armed Forces use
The US armed forces have a keen interest in treating severe hypovolemic shock on the battlefield because they lose many war fighters in this way who otherwise may have survived if better technology existed. PEG-20k is a promising option for military, first-responders, and trauma clinicians. The solution would have profound beneficial effects on far-forward resuscitative efforts in a prolonged field care scenario including mass-casualty scenarios where blood supply is limited.
Additionally, PEG-20k could reduce the need for fresh whole blood or blood products in the far-forward battle space, synergistically enhancing the resuscitative efficacy of blood products when used.
The new PEG-20k IV solution is expected to increase the time that a war fighter can safely stay in the low volume state after a massive hemorrhage 10 times longer than with conventional IV solutions (saline, Hextend, or whole blood).
If the average low volume time that a soldier can tolerate before needing definitive medical care (full resuscitation and surgery) is 60-120 minutes, then PEG-20k may provide expansion of the golden hour up to 24 hours based on large-animal pre-clinical models.